The Power of Placebos, Scientists have long been fascinated with placebos, which are inactive drugs or therapies that patients capacity to elicit genuine physiological and psychological benefits. New insights into the mechanics underlying this phenomena, particularly with regard to pain .
The Placebo Effect: An Overview
When a patient receives a treatment that has no therapeutic value and notices a noticeable improvement in their symptoms. .
Historical Context and Early Research
. However, the 20th century saw the start of methodical scientific research into placebos. Early research, with a human focus, demonstrated the effectiveness of expectations, conditioning, and the patient-doctor dynamic in inducing placebo reactions.
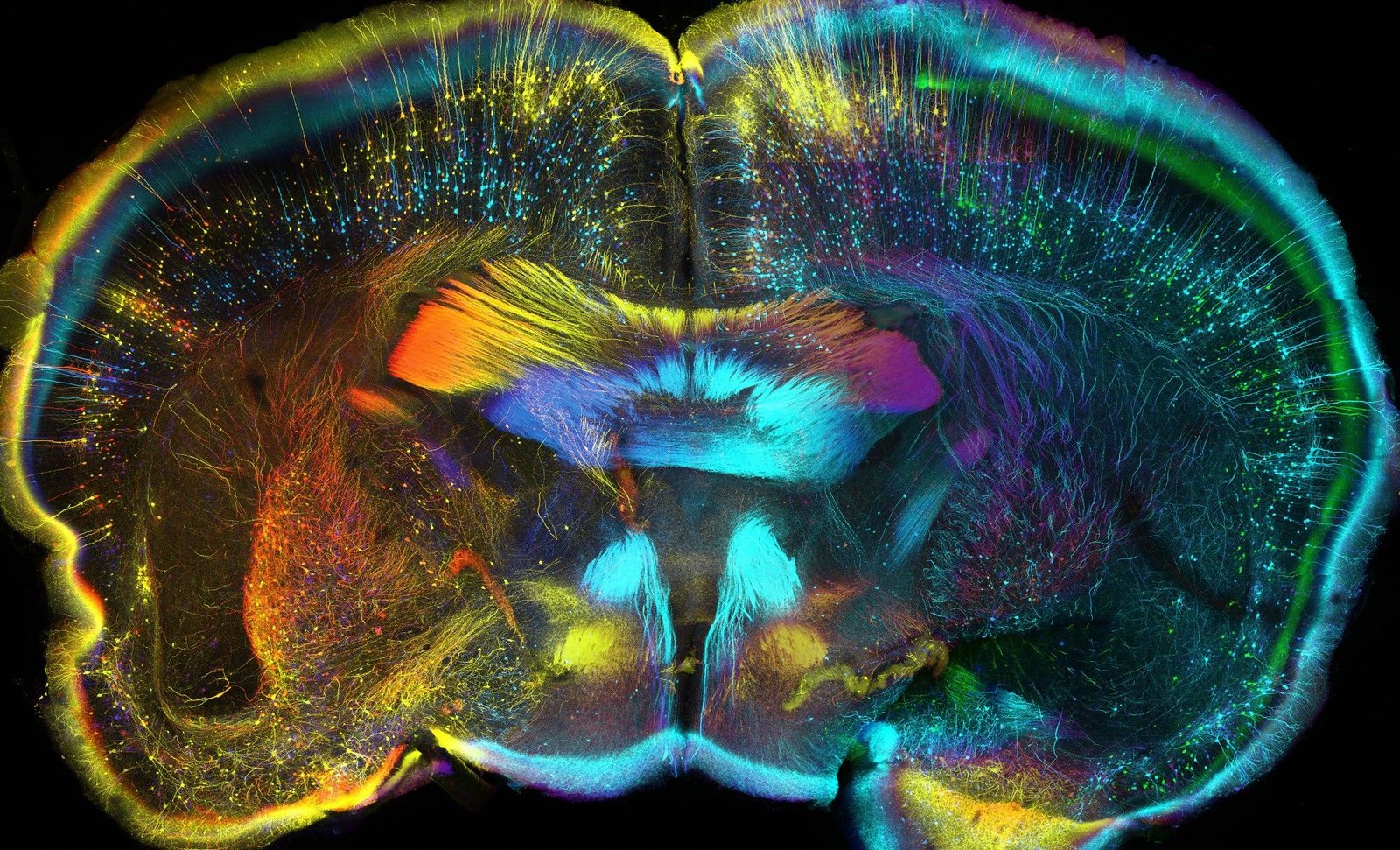
Recent Advances: The Mouse Brain Study
Novel insights into the brain mechanisms behind placebo-induced pain alleviation have been gleaned from a ground-breaking study conducted on mice. Researchers investigated how mice’s brains react to placebo treatments using genetic tools and sophisticated imaging techniques.

Mechanisms of Placebo-Induced Pain Relief
routes in the brain The function of neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and endorphins
Affected brain regions include the amygdala and prefrontal cortex.
Implications for Human Pain Management
Applying research from mice to people
Possible innovations in pain treatment techniques
ethical issues with the use of placebos
The Science of Pain
The perception of pain is complex and has both physiological and psychological aspects. But chronic pain, which lasts long after the original reason has disappeared, poses serious problems for both patients and medical professionals.

The Mouse Brain Study: Overview
Recent research on mice has provided fresh insight into the ways in which placebos can lessen pain.
The research used biochemical tests to evaluate changes in neurotransmitter levels and sophisticated imaging techniques to monitor brain activity.

Mechanisms of Placebo-Induced Pain Relief
.
It was discovered that when a placebo was administered, the body’s natural analgesics, endorphins, were released, simulating the effect of real analgesic medications. The prefrontal cortex and the amygdala, two brain areas involved in processing pain and controlling emotions, emit this chemical.
Implications for Human Pain Management
The understanding of the mouse brain obtained from this study has important consequences for the treatment of pain in humans. Through an understanding of the particular brain mechanisms underlying the placebo effect, to reduce pain without the use of drugs.
Enhancing patients’ placebo response through conditioning and expectation-based therapy is one such usage. These discoveries may also contribute to the creation of novel medications that target the identified pathways and relieve pain more effectively .

Case Studies and Real-World Applications
The potential of placebos in clinical settings is demonstrated by a number of real-world applications and case studies. .
Criticisms and Controversies
The use of placebos in pain therapy is not without controversy and criticism, despite the encouraging results. Critics contend that the placebo effect is essentially a psychological phenomena and that people with chronic pain may not get long-lasting relief from it.
It’s critical to balance evidence-based medicine with the usage of placebos. Although placebos can provide further pain relief, they should be used in addition to proven treatments rather than as a substitute for them.
Conclusion
The newest study on the brains of mice provides important new information on the complex neurobiological mechanisms involved in the pain-relieving effects of placebos.
There are still issues and moral dilemmas surrounding placebo use, but there is no denying that quality of life. The field of placebo-based therapy for pain management appears to have a bright future ahead of it, with new opportunities for efficient and compassionate care.
FAQs
What is the placebo effect?
This occurrence demonstrates how the mind can have an impact on physical health results.
What was the aim of the mouse brain study on placebos and pain?
By analyzing alterations in the mice’s brains following the administration of a placebo, the study sought to investigate the neurobiological mechanisms underlying the placebo effect’s ability to reduce pain. The goal of the study was to pinpoint the precise brain areas and neural pathways that are involved in pain alleviation brought on by placebo.
What are endorphins, and how do they relate to the placebo effect?
By attaching to opioid receptors in the brain, these neurotransmitters aid in the reduction of pain and promote feelings of wellbeing.
Can the findings from the mouse brain study be applied to humans?
Although extrapolating results from mice to people presents certain difficulties, the study offers insightful information that may guide novel pain management strategies. Comprehending the particular neural pathways in the brain responsible for the placebo effect can aid in the creation of treatments that utilize these pathways in people.
What is “open-label placebo,” and how does it work?
Research has indicated that patients can obtain notable symptom relief even when they are aware they are taking a placebo, highlighting the importance of expectation and belief.